
The spine can be divided into 4 parts: cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacral region. The cervical spine comprises of the first 7 vertebrae, which form the neck.

The lumbar spine is composed of the lower 5 vertebrae, which have been numbered L1–L5. The lowest vertebra of the lumbar spine (L5) is connected to the top of the sacrum, which is a triangular bone present at the base of the spine fitting into the two pelvic bones. In some cases, an extra or sixth lumbar vertebra may be present.

The thoracic spine is the central part of the spine, also called the dorsal spine, which runs from the base of the neck to the bottom of your rib cage. The thoracic spine provides the flexibility that holds the body upright and protects the organs of the chest.
Neck Pain

The most common cause of neck pain is injury to the soft tissues (muscles, ligaments or nerves) or prolonged wear and tear. Traumatic accidents or falls and contact sports can cause severe neck injuries and pain. Neck pain can also occur from infections, tumors or congenital abnormalities of the vertebrae.
Back Pain

Back pain or backache is the pain felt in the back that may originate from damage to the muscles, nerves, bones, joints or other structures in the spine. Back pain is one of the most common medical problems experienced by most people at some time in their life. It can be acute, usually lasting from a few days to a few weeks, or chronic, lasting for more than three months.
Degenerative Disc Disease
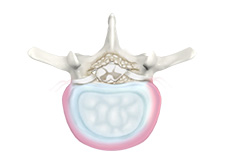
Degenerative disc disease (DDD) refers to the gradual deterioration of the intervertebral discs between the vertebrae. DDD is a misnomer as it is not actually a disease but a condition that affects the strength, resilience and structural integrity of the intervertebral discs due to advancing age, trauma, injury, repetitive movement, improper posture or poor body mechanics.
Spine Deformities

It is a condition where the spine or backbone is curved sideways instead of appearing in a straight line. It curves like an “S” or “C” shape. Larger curves cause discomfort while the small curves do not cause any problems.
Spinal Tumors

A spine tumor is the abnormal growth of uncontrolled tissues or cells in and around the spinal cord. Tumors can either be cancerous (malignant) or non-cancerous (benign). Tumors that begin in the spine are called primary spinal tumors. Tumors that spread to the spine from other parts such as the breast, prostate, lung, and other areas are called secondary spinal tumors.
Spinal Fractures

Vertebral compression fractures occur when the normal vertebral body of the spine is squeezed or compressed. The bone collapses when too much pressure is placed on the vertebrae, resulting in pain, limited mobility, loss of height, and spinal deformities. In severe compression fractures, the vertebral body is pushed into the spinal canal which will apply pressure on the spinal cord and nerves.
Spine Disorders

The spine is made up of a column of small bones called vertebrae that surround and protect the spinal cord and nerves that branch out from the spinal cord. Each bone or vertebra is separated from the other by a spongy tissue called an intervertebral disc, which acts as a cushion and prevents the bones from rubbing against each other during movement.
Spinal Instability

Spinal instability refers to the condition of failure of the spinal column to maintain its normal structure. Normally, the spine functions to protect and provide support to the body and its internal organs. An unstable spine is incapable of holding various spinal structures such as spinal muscles, ligaments, bones, and discs in place.
Spondylolysis

Spondylolysis is a stress fracture in the vertebra that may progress into spondylolisthesis, a condition where the vertebra gets displaced from the spinal column. Spondylolysis is the cause of frequent low back pain in children. It is more common among children and teenagers who participate actively in sports such as football, weightlifting, and gymnastics.
Sciatica

The sciatic nerve is the longest nerve in your body. It begins in the lower back and extends through the buttocks down the back of each leg to the thighs and feet.
Sciatica is a painful condition caused by the irritation of the sciatic nerve. Sciatica can be acute (short term), lasting for a few weeks or chronic (long term), persisting for more than 3 months.
Fractures of the Spine

A fracture of the spine is a break in the bone continuity of the spinal vertebrae or vertebral column. The spine extends from the neck to the lower back and consists of the vertebral bones which surround and protect the spinal cord. Damage to the spinal cord or spinal nerves can cause changes in sensation, strength, and other body functions.
Scoliosis

Scoliosis is a condition characterized by the abnormal curvature of the spine that causes a deviation to one side. It causes a physical deformity, making the spine look like the letter “C” or “S” instead of the letter “I”. Scoliosis can affect either the mid or lower back.
Kyphosis

Kyphosis is a condition of abnormal curvature of the spine that causes rounding of the upper back or a hunchback. The thoracic portion of the spine normally has a C-shaped curve, but excessive forward curve in the spine leads to kyphosis. Kyphosis most commonly affects the thoracic spine, but can involve the cervical and lumbar portions too.
Low Back Pain

Low back pain is often a common symptom of many disease conditions and the back pain may range from simple or dull pain to sudden and sharp pain. If the pain persists for a few days, it is acute pain whereas if it continues for more than 3 months, it is considered as chronic pain. In most cases, low back pain may resolve without any treatment, however, if it persists for more than 3 days, medical intervention is necessary.
Facet Joint Arthritis

Facet joints, also called zygapophyseal joints, are synovial joints located at the back of your spine, connecting the vertebrae together. Normally the facet joints are lined by a cartilage and a membrane of synovium. There are two joints between each pair of vertebrae located on either side of the spine. The facet joints provide stability for the spine.
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome

When this passageway becomes compressed, the condition is termed as thoracic outlet syndrome. It generally occurs within the age group of 20 to 60 years and is more common in females than in males.
Thoracic outlet syndrome can result due to injury, tumors that press nerves, poor posture that compresses nerves, weight lifting, anatomical defects such as an elongated C7 transverse process, anomalous tissue overgrowth, upper thoracic neurovascular compression, costocoracoid tendon, and subclavian muscle hypertrophy to name a few.
Neck Strains and Sprains

The neck is the most flexible part of the spine and supports the weight of the head. The unique anatomical structure of the cervical vertebrae allows the free movement of the head. The neck is also composed of muscles and ligaments. Any excessive stress on the ligaments and muscles may injure or damage them.
Disc Herniation

Disc herniation is a condition where the central nucleus pushes through the outer edge of the disc, causing a bulge that compresses the spinal nerves.
Aging, injury or trauma may cause the annulus fibrosus to tear, resulting in protrusion of the nucleus pulposus. This may compress the spinal nerves and/or spinal canal. The bulging disc may even break open, releasing the gelatinous material, which is a chemical irritant, causing inflammation of the spinal nerves.
Spine Trauma

Spine trauma is defined as an injury or damage to any region of the spine. The spine extends from the neck to the lower back and consists of the vertebral bones which surround and protect the spinal cord. Damage to the spinal cord or spinal nerves can cause changes in sensation, strength, and other body functions.
Spondylodiscitis

Spondylodiscitis is an infection of the intervertebral discs (between the vertebrae) along with the vertebrae (one of many small bones forming the spine). The condition is a primary infection of one or more intervertebral discs (discitis) with secondary infection of one or more vertebrae (spondylitis).
Spondylolisthesis

Spondylolisthesis is the displacement of the vertebral disc from the spinal column. Outward (forward) displacement is termed as anterolisthesis and inward (backward) displacement is termed as retrolisthesis. This condition is often preceded by spondylolysis, a degenerative condition of the vertebra.
Difficulty Walking

Walking is a complex interaction among multiple systems of the body. Proper walking is a result of balance, sensory function, reflexes, motor function, and many other systems working in conjunction.
Difficulty walking is defined as inability to walk properly due to abnormal and uncontrollable walking patterns. This can be attributed to factors such as genetics, neurological disorders, musculoskeletal disorders, injuries or other diseases.
Degenerative Spinal Conditions

A degenerative condition is a continuous deterioration of a tissue or an organ in your body over time.
Degenerative spinal conditions refer to a gradual loss of normal structure and/or function of the spine over time.
Benign Spinal Tumors

The spinal cord is a long bundle of nerves that extends from the brain along the length of the spinal column. The spinal cord is protected by the surrounding vertebrae and three membranes called the meninges. Spinal tumors are the result of abnormal, uncontrolled growth of tissues or cells in the spinal cord.
Pseudarthrosis/Nonunion

Pseudarthrosis is an unhealed broken bone, also known as nonunion. Usually, damaged or broken bones heal over time by forming new bone tissue connecting the damaged pieces of the bone. However, if the damaged bone fails to heal then it is called ‘nonunion’ or ‘pseudarthrosis’. Pseudarthrosis refers to the formation of a false bone due to improper healing.
Spinal Compression Fractures

A compression fracture of the vertebra occurs when the bones of the spine (vertebrae) collapse. Most commonly, these fractures occur in the thoracic or the middle portion of the spine.
A common cause of compression fracture in the spine is osteoporosis. This is a condition that makes the bones weak and unable to sustain normal pressure.
Spinal Injuries at Work

Injuries at the workplace are very common and may be debilitating. Global statistics report that around 260 million non-fatal injuries occur every year around the world of which 350,000 cases may suffer death. Workplace injuries often occur because of high-risk jobs, lack of or scarcity in safety devices, lack of training, and higher numbers of manual workers.
Arm Pain of Spinal Origin

Arm pain of spinal origin can be described as discomfort or pain felt anywhere in the arm including the wrist, elbow, or shoulder as a result of a pinched nerve (nerve compression) or irritated nerve in the spinal cord. The pain can occur as a dull constant pain or a sudden sharp pain that can develop suddenly or over time.
Scheuermann's Kyphosis

Scheuermann’s kyphosis is a deformity of the spine that develops during growth. It can be considered as increased kyphosis. Kyphosis is the C-shaped curving of the spine and is also known as hunchback. This deformity occurs in the junction between the thoracic region and lumbar sections of the spine or in the chest region.
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction

The most common symptom of sacroiliac joint dysfunction is pain. You may experience pain in the lower back, thigh, groin or buttocks that radiates down the leg. The pain is typically worse with standing and walking and is relieved on resting. Other symptoms include limping, fever, psoriasis, eye inflammation and limited range of motion.
Chordoma

Chordoma is a rare, slow-growing malignant tumor that develops in the spine and skull bones. It is thought to form from the remnants of the notochord (a preliminary structure present in a developing baby in the womb, which eventually forms the spinal cord).
Adjacent Segment Disc Disease

Spinal fusion surgery involves the fusion of two or more vertebral bones and is a standard of care for spinal deformities and conditions such as radiculopathy, myelopathy, and spondylolisthesis.
However, in the long-run, the surgery may be associated with adjacent segment disc disease, a complication in which the spinal segments above and below the fused portions develop abnormalities such as disc degeneration, instability, spinal stenosis or disc herniation.
Ankylosing Spondylitis

Sacroiliac joints are present in the lower back where the sacrum part of the vertebrae joins the iliac bones. The term ankylosis stands for loss of mobility of the spine, whereas spondylitis means inflammation of the spine. Therefore, ankylosing spondylitis is a condition where chronic inflammation of the spine and sacroiliac joint results in complete fusion of the vertebrae, leading to pain and stiffness in the spine.
Spondyloarthropathies

Spondyloarthropathies are a group of chronic inflammatory diseases of the spine and joints. Spondyloarthropathies can occur at any age, however, they occur more often in young males.
The most common spondyloarthropathies include ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and arthritis secondary to inflammatory bowel diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
Lordosis

The spine forms a natural curve at the neck, torso, and lower back, which allows it to absorb shock and hold the weight of your head. When this curvature is accentuated at the lower back, it is called lordosis. Lordosis may develop during childhood as a benign condition or later in life because of poor posture, osteoporosis, obesity, discitis (inflammation of the intervertebral discs) or spondylolisthesis (mal-alignment of the vertebrae).
Pathological Fractures of the Spine

Pathological fractures are broken bones in an area already weakened by another disease, not by an injury. Some underlying diseases can weaken the spinal bones making them brittle and eventually causing a fracture or break in the bone.
Vertebral Compression Fractures

Back pain is an indication of stress fractures known as vertebral compression fractures. Vertebral compression fractures occur when the normal vertebral body of the spine is squeezed or compressed. The bone collapses when too much pressure is placed on the vertebrae, resulting in pain, limited mobility, loss of height and spinal deformity.
Cauda Equina Syndrome

What Cauda equina syndrome is an emergency condition characterized by persistent severe lower back pain caused by the compression of a bundle of spinal nerves (cauda equina) at the end of the spinal cord (lower back and hip region). If not treated promptly, it can lead to permanent paralysis of the legs, or bowel, bladder, and sexual problems.
Spinal Infection

A spinal infection is described as an infection of the spine. It can occur in various locations of the spine i.e., intervertebral disc space, vertebral column, spinal canal, and nearby soft tissues.
Isthmic Spondylolisthesis

Isthmic spondylolisthesis is a spinal disorder in which one vertebra glides forward over the vertebra below. It usually affects the lumbar (lower back) spine, more frequently at L5-S1 levels (the fifth lumbar vertebra and first sacral vertebra).
Peripheral Nerve Compression

The human body has 2 nervous systems, the central nervous system that includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system that includes a network of nerves that lie outside the brain and spinal cord.
The peripheral nervous system transmits signals from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of your body.
Osteoporosis of the Spine
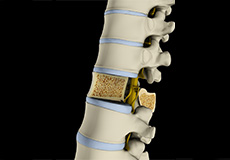
Osteoporosis is a bone disease characterized by a decrease in bone mass and density resulting in brittle, fragile bones that are more susceptible to fractures. The condition most commonly affects elderly women. Osteoporosis-related fractures are more common at the vertebral bodies of the spine. Osteoporosis is called a "silent disease," as a majority of the patients may be unaware of their condition until they develop a bone fracture.
Cervicogenic Headache

Cervicogenic headaches involve pain in one or both sides of your head that radiates from your neck to the front of the head.
Radiculopathy

Certain diseases or mechanical compression of these spinal nerves due to deformities in the vertebral column can lead to radiculopathy.
Radiculopathy is a condition where a nerve root in the spine is compressed, producing pain or weakness across the whole length of the nerve. It is sometimes referred to as a pinched nerve or sciatica. It occurs most commonly, but is not limited, to the lower back and neck.
Spina Bifida

Spina bifida is a congenital condition (birth defect) in which there is abnormal development of the back bones, spinal cord, surrounding nerves, and the fluid-filled sac that surrounds the spinal cord. This is a neurological condition that causes a section of the spinal cord and the surrounding structures to develop outside, instead of inside, the body. The defect can occur anywhere along the spine.
Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)

Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) is a condition that commonly affects the spine. It is characterized by calcification (bony hardening) of ligaments, tendons and joint capsule insertions. Usually, the upper portion of the back (thoracic spine) is affected, but it may also involve the neck (cervical spine) and lower back (lumbar spine). In a few cases, the elbow, patella, calcaneus, and hip and knee joints may also be affected.
Adult Degenerative Scoliosis

Adult degenerative scoliosis is characterized by side to side or lateral bending of the spine in adults. Degenerative scoliosis can involve either the mid-back and/or lower back region of the spine.
A host of different factors can alter the architecture of the spine and cause degenerative scoliosis.
Mid-back Pain

Mid-back pain is also called as thoracic pain or upper back pain. It occurs at the back of the chest and is much less common than lower back pain. It may occur due to poor posture, muscle strain, improper lifting and bending, physical inactivity, sports injury, a trauma in a car accident, cancer, or an autoimmune disease.
Poor Balance

Poor balance can be defined as a sense of unsteadiness on your feet due to dizzy spells or lightheadedness, fainting, blackouts, or loss of consciousness.
For proper balance, many body systems including muscles, joints, bones, vision, the balance organ in the inner ear, heart, nerves, and blood vessels should work normally.
Spinal Stenosis

Spinal stenosis is a condition caused by the vertebral column constricting and exerting pressure on the spinal cord or neural foramen (a bony tunnel through which a nerve exits the spinal cord).
Spinal Stenosis usually affects the cervical and lumbar spine. If the spinal canal is narrowed, the disorder is called cervical/lumbar central stenosis. If the foramen is narrowed, it is referred to as cervical/lumbar foraminal stenosis.
Discitis

Discitis, also called discitis, is inflammation between the spaces of the intervertebral discs in the spine. Intervertebral discs are located between the vertebrae and spaces between them are called intervertebral disc spaces. Swelling in these spaces puts pressure on the discs and results in pain. Chronic back pain is a rare complication of discitis. Discitis itself is relatively rare and usually affects young children.
Spine Bone Spurs

Spine bone spurs, also called osteophytes, are bony projections that develop in the spine’s facet joints where cartilage has worn out or along the vertebral body’s endplates edges. It can grow at any level of the spinal column such as the low and mid-back and in the neck.
Psoas Abscess

A psoas abscess is a rare medical condition that is defined as a painful collection of pus in the psoas muscle of the spine, located in the lower lumbar region of the spine. The muscle extends through the pelvis to the femur.
A psoas abscess can be categorized as primary or secondary based on the presence or absence of underlying disease.
Whiplash

Whiplash is a soft tissue injury to the neck, usually caused by a sudden forceful jerk commonly occurring because of an automobile accident, sports injuries or an accidental fall. Headache may develop immediately or after a short period of time after the injury. Sometimes, whiplash may also be referred to as neck strain, neck sprain or hyperextension injury.
Metastatic Tumors

A tumor (lump or mass) in your spine is an abnormal growth of tissue within or around your spinal column or spinal cord.
A metastatic tumor is a lump in your spine that is produced by cancer elsewhere in your body. It is the more common type of tumor in the spine. Though metastatic tumor can occur anywhere along your spine, most happen in your thoracic (mid-to-upper back) region.
Osteoporotic Fractures

Osteoporosis is a bone disorder where your bones become fragile and weak causing them to break easily. The condition occurs when your body starts losing bone or does not make enough bone or both, due to calcium deficiency. Osteoporosis is common in the spine.
Failed Back Surgery Syndrome

Failed back surgery syndrome is a term used to describe poor results from previous spine surgery.
The main goals of spine surgery are to relieve pain and improve spine stability. Pain is usually relieved by taking the pressure off a compressed spinal nerve.
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis

Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal lateral curvature of the spine, either to the left or to the right. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) is a type of scoliosis that occurs in children between 10 and 16 years of age. The term “idiopathic” means that the cause of scoliosis is unknown. The exact cause of idiopathic scoliosis is unknown in most of the cases, but there seems to be a genetic predisposition.
Idiopathic Scoliosis

Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal lateral curvature of the spine, either to the left or to the right. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) is a type of scoliosis that occurs in children between 10 and 16 years of age. The term “idiopathic” means that the cause of scoliosis is unknown. The exact cause of idiopathic scoliosis is unknown in most of the cases, but there seems to be a genetic predisposition.
Epidural Abscess

An epidural abscess is a medical condition that can be defined as an infection in the region between the spine, or bones of the skull, and the membranes that surround the spinal cord (meninges) and brain.
If the infection is located inside the skull region, it is called an intracranial epidural abscess. If the infection is in the spine region, it is called a spinal epidural abscess.
Sagittal Imbalance

The spine has three natural curves when viewed from the side, an inward curve in the neck and lower spine called lordosis and an outward curve in the mid-back called kyphosis. Normal spine curvature keeps your head in line with your pelvis so that the stresses on your spine are well balanced.
Adult Kyphosis-Types and Causes

Postural kyphosis is the result of poor posture and is common in adolescents and younger adults. Slouching posture when sitting or standing tends to cause the spine to curve forward.
It is often associated with hyperlordosis of the lumbar portion of the spine.
Back Pain in Children

Back pain is uncommon in children and is usually associated with a serious underlying condition or an injury. Often, the cause of back pain is non-specific and is thought to be due to musculoskeletal strain, poor posture, heavy school bags that are not worn correctly or underlying mood problems.
Piriformis Syndrome

Piriformis Syndrome is an uncommon, rare neuromuscular condition caused by the compression of the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle. The sciatic nerve is a thick and long nerve that passes below or through the piriformis muscle and goes down the back of the leg and finally ends in the feet in the form of smaller nerves.
Disc changes

The cartilaginous disc is made up of an outer fibrous layer called the annulus fibrosus, which surrounds an inner gelatinous core called the nucleus pulposus. The nucleus pulposus is well hydrated and acts as a shock absorber. Over time, the nucleus pulposus begins to dehydrate and become stiffer, losing its functionality as a shock absorber.
Cervical Fracture

The neck is made up of seven tiny bones called cervical vertebrae (C1-C7). These are protected by spongy vertebral discs present between them and supported by ligaments that hold them together and surround the underlying spinal cord.
Cervical Deformities

The spine is made up of 33 small bones called vertebrae and is known as the spinal column or vertebral column. It can be divided into 5 parts: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccyx region. The cervical spine is comprised of the first 7 vertebrae, which supports the neck and the head. Any abnormality in the alignment, shape, or formation of the cervical vertebral column is called cervical spine deformities.
Cervical Spondylosis

Cervical spondylosis, also called arthritis of the neck, is an age-related medical condition characterized by deterioration of spinal joints, vertebrae, discs, and ligaments in your neck.
Cervical Stenosis

Cervical stenosis refers to the narrowing of the spinal canal that protects the spinal cord and its branching nerves.
Cervical stenosis develops after age 50 because of aging and spinal wear and tear. Some patients have a history of back injury or trauma.
Cervical Disc Herniation

Cervical disc herniation can arise due to aberrations of the intervertebral disc such as bulging, rupture, and slipped or extruded disc. It results in neck, shoulder, and arm pain. In some cases, a disc herniation may occur due to injury, repetitive movements, or degenerative disc disease (DDD). In DDD the disc strength, resiliency, and structural integrity are affected due to advancing age, trauma, injury, smoking, poor diet, improper posture, or poor body mechanics.
Cervical Degenerative Disc Disease

Cervical degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a misnomer, as it is not a disease as such but a condition that affects the strength, resiliency and structural integrity of the intervertebral discs due to increasing age, trauma, injury, repetitive movement, improper posture, or poor body mechanics. Cervical DDD is commonly seen in adults after 50 years of age and most of them are usually not aware about their condition until they are examined for some other health condition.
Cervical Radiculopathy/Myelopathy

The spine, also called the backbone, is designed to give us stability, smooth movement, as well as provide a corridor of protection for the delicate spinal cord. It is made up of bony segments called vertebrae and fibrous tissue called intervertebral discs.
Cervical Disc Protrusion

Cervical disc protrusion, commonly known as a disc bulge, occurs when the spinal discs and associated ligaments are intact, but may form an outpouching that presses on the spinal nerves.
Lumbar Stenosis

Lumbar stenosis is the compression of spinal nerves caused by the narrowing of the spinal canal. It is one of the common causes of lower back pain. Spinal stenosis can also affect the spine in the neck region.
One of the causes of spinal stenosis is aging. Other causes include Paget’s disease, achondroplasia, spinal tumors, and spinal injuries.
Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease

The normal intervertebral disc is composed of a nucleus pulposus at the center, surrounded by a fibrous ring known as annulus fibrosus. The nucleus pulposus is a soft, well hydrated, jelly-like substance that acts as a shock absorber.
Lumbar degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a common cause of lower back pain. Over time, these natural shock absorbers wear out and degenerate. Degenerative disc disease is not actually a disease but refers to the changes in the spine that occur as a part of the normal aging process.
Lumbar Disc Herniation

The lumbar intervertebral discs are flat and round, present between the lumbar vertebrae and act as shock absorbers when you walk or run. There is a soft, gelatinous material in the center (nucleus pulposus) which is encased in strong elastic tissue that forms a ring around it called annulus fibrosus.
Lumbar Facet Joint Arthropathy

There are two facet joints present between each pair of vertebrae, one on either side of the spine. Facet joints are synovial joints comprised of small, bony knobs arranged along the back of your spine. Two vertebrae are connected to each other through these knobs and form a facet joint. These joints are covered by a soft tissue called articular cartilage, which allows the smooth movement of the bones.
Lumbar Radiculopathy

The spine consists of 33 vertebral bones stacked one on top of the other with cushioning discs lying between each vertebra. The lumbar region of the spine (below the rib cage) consists of 5 vertebrae. Nerves of the spinal cord in this region communicate with the lower body through spaces between the vertebrae.
Fracture of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine

The backbone is made of small bones arranged from the neck down to the buttocks, one above the other. The region at the chest and lower back are called the thoracic and lumbar spine, respectively. These are the two regions commonly affected by a fracture.
Thoracic Disc Herniation

Thoracic herniation disc is a condition in which the outer fibers (annulus) of the intervertebral disc are damaged causing the soft inner material of the nucleus pulposus to rupture out of its space. This condition can be extremely serious if it occurs in the thoracic spine. Thoracic disc herniation is a relatively uncommon condition.
Thoracic Myelopathy

Thoracic myelopathy is a disorder resulting from severe spinal cord compression in the thoracic region. The spinal cord in this region typically gets compressed as a result of bulging or herniated discs, spinal trauma, or bone spurs causing severe pain and discomfort. Thoracic decompression surgery is one of the effective ways to treat thoracic myelopathy.
Compression of Thoracic Nerve

Nerves can undergo compression or become pinched by surrounding structures as they emerge from the spine, a condition called radiculopathy. Nerve compression mostly occurs in the neck or lower back regions which have more mobility, but it can sometimes involve the upper back or thoracic region. Thoracic nerve compression may be associated with numbness, tingling sensation and pain around the chest and upper back. Leg weakness may also be present.
Fracture of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine

The backbone is made of small bones arranged from the neck down to the buttocks, one above the other. The region at the chest and lower back are called the thoracic and lumbar spine, respectively. These are the two regions commonly affected by a fracture.
Lumbar Radiculopathy

Back pain is a common condition affecting approximately 80% of the population at some point in their lives. The area usually affected is the lower back (lumbar region) as it bears most of the upper body’s weight. Trauma to the spine, age and overuse can result in deterioration of the vertebral bones and joints or bulging of the discs.
Fracture of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine

The backbone is made of small bones arranged from the neck down to the buttocks, one above the other. The region at the chest and lower back are called the thoracic and lumbar spine, respectively. These are the two regions commonly affected by a fracture.
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery

Minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS) is the latest technology available to perform spinal surgeries through small, less than one-inch-long incisions. It involves the use of special surgical instruments, devices and advanced imaging techniques to visualize and perform the surgery through such small incisions.
Vertebroplasty

Vertebroplasty is a minimally invasive procedure performed to reduce or eliminate pain caused by a vertebral compression fracture. It stabilizes the fracture and prevents further collapse of the vertebra, averting deformity.
Laminectomy

Degeneration of the facet joints and intervertebral discs results in the narrowing of the spinal canal, known as spinal stenosis. In addition, the arthritic facet joints become bulkier and consume the space available for the nerve roots. Besides, bony outgrowths, also known as bone spurs or bone osteophytes can also narrow the spinal canal.
Anterior Cervical Discectomy with Fusion

The vertebrae of the backbone are cushioned by intervertebral discs that act as shock absorbers and allow frictionless movement of your back. It is made up of a soft gel-like center called the nucleus pulposus that is surrounded by a tough outer ring of annulus fibrosus. A herniated disc is a condition in which the nucleus pulposus bulges out through the damaged or broken annulus fibrosus.
Spine Injections

Spine injection is a non-surgical treatment modality recommended for the treatment of chronic back pain. Injection of certain medicinal agents relieves the pain by blocking the nerve signals between specific areas of the body and the brain. The treatment approach involves injections of local anesthetics, steroids, or narcotics into the affected soft tissues, joints, or nerve roots. It may also involve complex nerve blocks and spinal cord stimulation.
Nerve and Spinal Decompression Surgery

Neck and lower back pain are some of the most common symptoms experienced by patients in today’s society. Sometimes this pain is simply localized to the spine, but occasionally it can differ and include numbness, tingling sensations, and weakness traveling down into the arms and/or the legs. While the onset of these symptoms will vary from patient to patient, the underlying cause of the pain is often due to compression of the spinal nerves.
Kyphoplasty

Osteoporosis (bone disease) is the primary cause of vertebral compression fractures. Other causes include trauma such as a fall or motor vehicle accident and some types of cancers affecting the spinal vertebrae.
Balloon kyphoplasty is a spine surgery that relieves back pain caused by a vertebral compression fracture. The aim of balloon kyphoplasty is to relieve pain, stabilize the fracture and restore the vertebral body height.
Spinal Fusion

Spinal fusion is the surgical technique of combining two or more vertebrae. A fusion of the vertebrae involves the insertion of secondary bone tissue obtained either from an autograft (tissues from your own body) or allograft (tissues from another person) to enhance the bone healing process.
Scoliosis Surgery

Surgery for scoliosis is recommended when the spinal curvature is severe and is either worsening or is a cause of severe pain or difficulty in breathing. The surgery is aimed at rectifying the spinal curvature, stabilizing the spine and preventing it from worsening. The rectification of the curved spine involves the removal of one or more intervertebral discs (disectomy), vertebrae, or spinous processes from the curved segment of the spine.
Lower Back Pain Surgery

Lower back pain can be disabling; however, most cases heal with time (2-12 weeks) and with conservative therapy. However, surgery is suggested when symptoms persist and begin to affect your daily activities.
Neck Surgery

Neck surgery is a surgical procedure employed for the treatment of neck pain when conservative measures such as physical rehabilitation, medications, and rest have failed to provide any relief to your neck pain.
The neck supports and assists in movement of the head. It is the most flexible part of the spine and consists of 7 cervical vertebrae, cervical segment of the spinal cord, spinal nerves, ligaments, tendons and muscles.
Scoliosis Treatment

Scoliosis is the abnormal curvature of the spine giving the spine an “S” or “C” shape. Scoliosis can occur at any age and is more common in girls than boys. Larger curves cause discomfort while the smaller curves do not cause any problems. In most cases, the exact cause remains unknown.
Spine Deformity Surgery

The spine or backbone provides stability to the upper part of the body. It helps to hold your body upright. It consists of several irregularly-shaped bones called vertebrae appearing in a straight line. The spine has two gentle curves when seen from the side and appears to be straight when viewed from the front.
Radiofrequency Ablation

Radiofrequency ablation (RFA), also called rhizotomy or neurotomy, is a novel non-surgical technique of treating pain. This technique employs radiofrequency waves to produce heat and the heat produced damages the nerves transmitting pain signals to the brain. This procedure is performed to treat painful facet joints in the spine that usually cause chronic low back pain and neck pain.
Spinal Cord Stimulator

A spinal cord stimulator is a device that sends electrical impulses to the areas of the spinal cord causing pain and interferes with the transmission of pain signals to the brain. It blocks the brain's ability to sense pain in the stimulated areas, thus relieving pain without the side effects that medications can cause. The electrical impulses can be targeted to specific locations and, as pain changes or improve, stimulation can be adjusted as necessary.
Robotic Spine Surgery

Robotic spine surgery is a procedure where your surgeon is assisted by a robotic system to perform surgery to the spine. Precision is very important when performing spine surgery. Robotic systems are becoming increasingly popular in the medical fraternity as it offers better precision and reduces the risk of complications associated with conventional surgery. Your doctor can use robotic assistance while performing an open or minimally invasive procedure.
Scoliosis Correction with Spinal Monitoring

Scoliosis is a condition characterized by the abnormal curvature of the spine. The abnormality can be surgically corrected by fusing the affected parts of the spine so that they grow into a solid bone and do not twist. During the surgery, your doctor makes an incision to expose the spine. Using X-ray guidance, your doctor fixes rods with the help of screws or hooks to bring the spine into the correct position and stabilize it until it grows and fuses.
Posterior Scoliosis Surgery

The spine is the backbone of the body. It naturally curves a little. This allows us to walk, move, and balance ourselves properly. But some people have a spine that curves too much to one side. This condition is called scoliosis. Scoliosis usually has no symptoms. In severe cases, the body looks asymmetrical with uneven hips or shoulders. Severe scoliosis may also cause backache and could contribute to other health problems.
Revision Spinal Surgery

Revision spine surgery is surgery performed in certain patients to correct the problems of earlier spine surgery.
Revision surgery is indicated in patients with chronic pain even after surgery.
Endoscopic Spine Surgery

Endoscopic spine surgery is considered as a last resort for treating spinal conditions in the neck and back when conservative treatments have failed to improve your symptoms.
Fracture Stabilization

A spinal fracture refers to a break in any of the bones that make up the spine. It can occur due to trauma such as a traffic accident, fall from a significant height or weakening of the bones due to osteoporosis or a tumor. The thoracic or lumbar spine (upper and lower back) are the most common locations for spinal fractures.
Spine Osteotomy

Severe spinal deformity may occur in conditions such as Scheuermann's kyphosis, iatrogenic flat back, post-traumatic, neuromuscular, congenital and degenerative disorders, and ankylosing spondylitis. Severe deformity causes symptoms that may include a subjective sense of imbalance, leaning forward (stooping), early fatigue, intractable pain, and difficulty in a horizontal gaze.
Spinal Infection Debridement

The spine is made up of bones called vertebrae which surround and protect the spinal cord. These are separated by intervertebral discs which provide cushioning between the vertebral bones. A spinal infection may affect any part of your spine, i.e. the vertebral column, intervertebral discs or the soft tissues surrounding the spine.
Tumor Decompression

In medicine, decompression is a surgical procedure involving the excision or repositioning of a structure compressing any other structure in your body in order to relieve the pressure.
Spinal decompression refers to various procedures intended to relieve painful pressure on the spinal cord and/or nerve roots caused by compression from another structure.
Tumor Stabilization

Tumor stabilization is a surgical procedure performed to strengthen and support your spine when it is weakened or in danger of breaking due to a tumor growth. It is typically carried out after a surgery called tumor decompression, which involves the removal or shrinking of the tumor.
Adult Scoliosis Correction

Adult scoliosis is the abnormal curvature of the spine giving the spine an “S” or “C” shape in a skeletally mature person. Larger curves cause discomfort while smaller curves usually do not cause any problems. In most cases, the exact cause remains unknown.
Anterior and Posterior Scoliosis Surgery

The spine is the backbone of the body. It naturally curves a little. This allows us to walk, move and balance ourselves properly. But some people have a spine that curves too much to one side. This condition is called scoliosis. In most cases, especially in children and adolescents, the cause of scoliosis is unknown and scoliosis is referred to as idiopathic scoliosis.
Transforaminal Epidural Block

An epidural block or epidural spinal injection is a non-surgical treatment option for relieving back pain and other symptoms.
Epidural blocks contain a strong anti-inflammatory agent called corticosteroid and an anesthetic for pain relief. It is administered into the epidural space of the spine, the space between the outermost covering of the spinal cord (dura mater) and the wall of the spinal canal.
Discography

Discography or a discogram is a procedure to evaluate back pain. It helps identify a painful spinal disc.
The spinal column consists of vertebral bones stacked one on top of the other that surround and support the spinal cord. Spinal nerves pass through spaces between the vertebrae to communicate with the rest of the body. Spinal discs are soft discs present between the vertebral bones that act as shock absorbers and help keep the spine flexible.
Spinal Infection Decompression

The spine is made up of bones called vertebrae which surround and protect the spinal cord. These are separated by intervertebral discs which provide cushioning between the vertebral bones. A spinal infection may affect any part of your spine including the vertebral column, intervertebral discs or the soft tissues surrounding the spine.
Spinal Infection Stabilization

The spine is made up of many bones called vertebrae which surround and protect the spinal cord. Intervertebral discs between the vertebral bones provide cushioning. A spinal infection may affect any part of the spine including the vertebral column, intervertebral discs or the soft tissues surrounding the spine.
Minimal Exposure Tubular Retractor (METRx) System

Minimally invasive surgery is a technique of performing surgeries through tiny incisions and is an alternative to open surgery. Moreover, minimally invasive surgery offers certain advantages over open surgery.
Minimally invasive surgeries are done by using various techniques and the Minimal Exposure Tubular Retractor (METRx) system is a more evolved technology than a microendoscopic discectomy system.
Removal of Facet Joint Cyst

Facet joint cysts, also called synovial cysts, are benign, fluid-filled sacs that develop due to degeneration of the facet joints of the spine. These cysts normally occur in the lumbar spine (lower back) area and may not cause problems, but when large enough, they can cause spinal stenosis or narrowing of the spinal canal leading to compression of the spinal cord or spinal nerves.
Spinal Manipulation

Spinal manipulation is a non-surgical "hands-on" technique in which professional chiropractic specialists use leverage and exercises to adjust spinal structures and restore mobility of the back. During pain, the nerve that is interconnected with the muscles, joints, bone becomes weak and loses its ability to function. With this therapy, the nerve will be made to work normally and the blood circulation in these areas also increases.
Spondylolisthesis Reduction & Fusion

Spondylolisthesis is a condition characterized by the displacement of one vertebra over the other. Excessive displacement may compress the surrounding spinal nerves and cause pain.
Treatment depends on the age, the extent of the slip, and the severity of symptoms. Surgery is an option if daily activities are difficult to perform because the vertebra continues to slip and the pain does not improve with conservative treatment.
Outpatient Spine Surgery

Outpatient spine surgery is an operative procedure that does not require an overnight stay at the hospital. It is also called ambulatory or same-day surgery. Improvement in surgical techniques, modern pain management, and rehabilitation protocols allows surgeons to perform certain operative techniques of the spine (from cervical to lumbar region), with a minimally invasive technique on an outpatient basis.
Foraminoplasty

Neural foramina are small canals at every level of the spine through which nerves leave the spinal cord and go to the limbs and other parts of the body. Narrowing of this canal is called foramina stenosis. The narrowing may be caused by bone spurs, a herniated or bulging disc, arthritis, ligament thickening or enlargement of a joint in the spinal canal.
Sacroiliac Joint Minimally Invasive Fusion

Inflammation or irritation of the SI joints may cause pain in the lower back, abdomen, groin, buttocks, or legs. Minimally invasive SI joint fusion is a procedure designed to stabilize the SI joints by grafting the sacrum to the ilium using instrumentation, bone graft, or both in order to fuse the bone, limiting movement. When both SI joints require surgery, one joint is treated first and the second joint surgery is scheduled after complete recovery from the first one.
Transpedicular Approach Surgery

The vertebral column is made up of individual bones (vertebrae) stacked one above the other. These are protected by spongy intervertebral discs that cushion the spine during movements such as lifting, running, and jumping. Degeneration, diseases, and trauma to these discs can cause them to herniate (bulge) beyond the level of the vertebrae, compressing the adjacent spinal cord and causing pain, numbness, weakness, and changes in bladder and bowel functions. The transpedicular approach is a surgical procedure to treat thoracic disc herniation.
Treatment Options for Back and Neck Pain

Back and neck pain is common symptoms of injury, damage, deformity, or unhealthy spinal conditions. Pain may range from a mild ache to a sharp shooting pain that can spread down your arms and legs. There are many conservative and surgical treatment options that can relieve pain by targeting the symptoms or the underlying problem.
XLIF - Extreme Lateral Interbody Fusion

Extreme lateral interbody fusion (XLIF) is a minimally-invasive surgery that involves the fusing of two degenerative spinal vertebrae. The procedure is conducted to relieve painful motion in the back caused by spinal disorders.
Disc Decompression

The spinal cord passes through the vertebral column, which forms a bony protective cover. Between the vertebral bones are soft discs that cushion the spine against stresses and allow the spine to be flexible.
Acute or chronic injury can cause a spinal disc to herniate or rupture. The damaged disc may compress against the spinal cord or the nerves that branch out through the vertebral bones, leading to pain, loss of sensation and/or motor function in the part of the body supplied by the nerve.
Endoscopic Rhizotomy

Endoscopic rhizotomy is a minimally invasive procedure to destroy nerves that transmit pain impulses from the facet joints of the spine. Your surgeon uses an endoscope (a narrow tube with a tiny camera) to identify the nerves and destroy them.
Mazor Robotic Renaissance

Mazor Robotic Renaissance® is a surgical guidance system that assists your surgeon in performing minimally invasive spine surgeries.
The Renaissance system is indicated in patients suffering from degenerative disc conditions, kyphosis, scoliosis, spinal canal narrowing, spondylolisthesis, and vertebral compression fractures.
Image-Guided Spine Surgery

The spine is a complex 3-dimensional structure that is interspersed with a complex lattice of delicate blood vessels and nerves. Trauma to these structures during surgery is a big concern in spinal surgery. The complexity and increased need for precision in thoracic spine surgeries have led to the introduction of computers to assist in many spinal procedures.
Intracept - Basivertebral Nerve Ablation

Intracept is a minimally invasive procedure developed by Relievant to treat chronic low back pain by targeting the basivertebral nerve.
The basivertebral nerve enters the vertebral bodies of the spinal column. Within the vertebral body, the nerve branches and supplies the endplates or the upper and lower surfaces of the vertebral body.
Minimally Invasive Discectomy and Decompression

The spinal cord passes through the vertebral column, which forms a bony protective cover. However, many conditions can cause parts of the vertebrae to compress the spinal cord or the nerves that branch out through them, leading to pain, loss of sensation and/or motor function in the part of the body supplied by the compressed nerve. Minimally invasive discectomy and decompression is a surgical procedure to release pressure on the compressed nerve and restore function.
Spinal Tumor Surgery

A spinal tumor is an abnormal mass of tissue surrounding or found within your spinal cord and/or spinal column.
Treatment for a spine tumor may be nonsurgical or surgical depending on the characteristics of the tumor and your overall health.
Complex Spine Surgery

Complex spine surgery is a procedure that involves six or more vertebrae of the spinal column, requiring six or more hours of surgery to correct a spinal deformity. Complex spine surgery is very difficult to perform and demands the highest level of patient dedication to be successful.
Surgery for Scoliosis

Surgery for scoliosis is recommended when the spinal curvature is severe and is either worsening or is a cause of severe pain or difficulty in breathing. The surgery is aimed at rectifying the spinal curvature, stabilizing the spine and preventing it from worsening. The rectification of the curved spine involves removal of one or more intervertebral discs (discectomy), vertebrae or spinous processes from the curved segment of the spine.
IDET (Intradiscal Electrothermal Annuloplasty)

The bones (vertebrae) of the backbone are separated by spongy discs that cushion and act as shock absorbers to the backbone. With age, these discs can wear-out and tear. This causes the adjacent nerves to come in contact with the central part of the disc (nucleus), or the nucleus to move out and press against the adjacent nerves, leading to irritation and pain. Intradiscal electrothermal annuloplasty (IDET) is a treatment for chronic lower back pain related to spinal disc damage or degeneration.
How to prevent Back Pain

Back pain is common and usually affects everyone at some point. It often occurs more frequently as you grow older. Pain can either be sharp and sudden or dull and constant. Acute back pain lasts a few days or weeks while pain that lasts more than 6 months is considered chronic. Adopting a few good habits and taking certain precautions can help prevent back pain.
Lateral Extracavitary Approach Surgery

Many approaches have been introduced in spinal surgery to gain optimal access to the injured or diseased area, with minimal or no damage to surrounding tissues. There are three main approaches – anterior (from the front), posterior (from the back) and lateral (from the side). Because of the complexity of the structure of the spine, and potential complications involved with surgery, most of these approaches are very challenging to perform.
Excelsius GPS Robotic Navigation

ExcelsiusGPS® Robotic Navigation system is the latest technology designed to integrate the benefits of robotics and navigation into one platform to provide minimally invasive spine surgery and optimize patient care with improved accuracy and safety.
ExcelsiusGPS enables surgeons to perform spinal surgical procedures with a high degree of accuracy while making them significantly less invasive than a traditional open surgical approach.
Methylene Blue for Intradiscal Pain

Methylene blue is a low-molecular-weight chemical dye that possesses anti-inflammatory properties. It is used to treat irritated intervertebral discs and is effective in minimizing and treating discogenic (involving one or more intervertebral discs) low back pain.
Spinal Decompression Therapy

Spinal decompression therapy involves stretching your spine using a manual or motorized traction table to help ease neck, back, or leg pain. It is a non-surgical technique to relieve pressure on your spinal discs and spinal nerves. Spinal traction is also believed to improve the supply of blood, oxygen and nutrients to the spine to promote healing.
Neuromodulation

Pain is an unpleasant sensation caused by illness or injury. Pain can have a negative impact on a person's quality of life. Chronic pain is the pain that is constant and persists for long periods of time. The treatment options for chronic pain include medications, surgical interventions, physical therapy, and psychotherapy.
Minimally Invasive Scoliosis Surgery

The goal of scoliosis surgery is to both reduce the abnormal curve in the spine and to prevent it from progressing further and getting worse. To achieve this, a spinal fusion is performed to fuse the vertebrae, in the curve to be corrected. This involves placing bone graft or bone graft substitute in the intervertebral space between the two vertebrae. Instrumentation such as rods and screws are also used to realign and stabilize the vertebrae until the graft heals and fuses the two vertebrae together.
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery for Spondylolisthesis

Coming soon
Superion

Superion®, a product of VertiFlex, Inc., is an FDA-approved, minimally invasive procedure to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
Lumbar spinal stenosis is a degenerative disease that causes the narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal and compression of the spinal nerves.
Spinal Nerve Blocks

A spinal nerve block is the injection of an anesthetic and steroid medication around the spinal nerve root to diagnose or treat pain.
Spinal nerve blocks are indicated to relieve pain, weakness, numbness and tingling sensations in your neck, back, and extremities due to nerve injuries such as a pinched nerve or narrowing of the spinal column (stenosis).
Spinal Facet Rhizotomy

Spinal facet rhizotomy is a minimally invasive procedure to destroy nerves that transmit pain impulses from the facet joints of the spine.
Facet joints are the joints between the different vertebra of the spine. There are two joints on either side from the neck to the lower back.
Percutaneous Vertebroplasty

Percutaneous vertebroplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to treat fractures of the spinal vertebral bones. During this procedure, your doctor inserts a needle through your skin into the fractured vertebra and injects bone cement. The cement hardens and provides strength and stability to the vertebra.
Dorsal Column Stimulator

The dorsal column stimulator (DCS) or spinal column stimulator is a device that relieves chronic pain associated with spinal nerves through electrical stimulation. It is used to treat chronic disabling pain such as failed back surgery syndrome and complex regional pain syndrome, which show little or no improvement with other treatments such as medication or surgery.
Physical therapy for the Spine

Physical therapy is one of the foremost necessary treatment modes of recovery for back pain. A referral to physiotherapy sometimes is created by your spine surgeon. A physical therapist is a well-trained, skilled health care professional who facilitates improving movement and manages the pain by safe stretching, conditioning, and strengthening exercise techniques. Patients are guided concerning the fundamental anatomy of the body and their mechanism of action. They are also instructed about the varied exercise regimens to extend the activity level thereby strengthening the muscles.
Non-Surgical Spine Treatments

In most cases, back pain can be resolved without surgery. The conservative treatment involves the use of pain medications and other methods to reduce inflammation and restore normal function. Usually, some self-care methods and medications can help to overcome back pain, but if pain and inflammation persist over 72 hours, it is necessary to consult your physician.
Facet Injections

The facet joints are the tiny joints situated at the upper and lower part of each vertebra, connecting one vertebra to the other. Each vertebra has four facet joints: a pair that connects to the vertebra above (superior facets) and another pair that connects to the vertebra below (inferior facets). They guide motion and provide stability.
Epidural Spinal Injection

Epidural spinal injection is a non-surgical treatment option utilized for relieving back pain. Spine degenerative conditions such as herniated disc, spinal stenosis and many others may induce back pain due to the compression of the associated spinal nerves. This pain or numbness may extend to the other parts of the body such as hips, buttocks, and legs.
Epidural Steroid Injections

Epidural steroid injection (ESI) is a minimally invasive approach to treat inflammation of spinal nerves that causes pain in the neck, arms, back and legs. This technique may help relieve back pain in conditions such as spinal stenosis, spondylolysis or herniated discs.
Medial Branch Block Injections

Facet joints are the joints connecting the different vertebrae of the spine to each other. Medial branch nerves are small nerves that supply the facet joints of the spine.
A medial branch block is an injection of a local anesthetic administered near the medial branch nerves to temporarily block the pain signal carried from the facet joints of the spine to the brain.
Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection

The epidural space of the spine is the area between the vertebral bones and the protective dura sac that surrounds the spinal cord and nerves.
A steroid injection consists of an anti-inflammatory medication called a corticosteroid, that is combined with an anesthetic and injected into the body to relieve pain and inflammation.
In-Office Cervical Injections

In-office cervical injections are administered in a medical office or clinic setting to provide relief from pain or inflammation affecting the neck and upper back. The injection is made in the patient’s epidural space, which is the area between the outermost covering of the spinal cord, the dura mater, and the wall of the spinal canal. It runs along the length of your spinal cord, is approximately 5 mm wide and is filled with spinal nerve roots, fat, and blood vessels.
Caudal Epidural Injection

The epidural cavity is the space surrounding the spinal cord, which extends from the skull to the tailbone, and consists of fat, nerves and blood vessels. Nerves in this space can be blocked by injecting an anesthetic, or a constricted nerve can be relieved of pain and inflammation by injecting a steroid medication into the epidural space. Caudal epidural injections are administered at the spinal segments of the lower back and tail bone.
Non-Surgical Treatment for Disc Disease

The spinal column consists of vertebral bones stacked one on top of the other, surrounding and protecting the spinal cord. Soft cartilaginous discs present between the vertebrae support the spine, act as cushions against stress and permit spine mobility. These discs can undergo damage or degeneration with age, overuse or injury, and is referred to as disc disease. This can result in the narrowing of the disc space and compression of spinal nerves.
Piriformis Muscle Injection

The piriformis muscle is present in the buttocks, connecting the sacrum to the outer surface of the hip. This muscle enables us to walk and run. The sciatic nerve is a thick, long nerve passing through or below the piriformis muscle.
A spasm of the piriformis muscle can compress the sciatic nerve, leading to severe pain (sciatica). The pain is usually felt over the buttocks but may radiate to the back of the thigh and down the leg as well.
Thoracic Facet Joint Injection

Facet joints are small joints present between the vertebral bones including the vertebral bones of the thorax (upper back). The bones in these joints are covered by cartilage and a capsule filled with synovial fluid surrounds the joint reducing friction. Thoracic facet joints can be affected by injury, mechanical stress or arthritis causing pain in the mid-back, chest and rarely the arms.
Costo-vertebral Joint Injection

Costo-vertebral joint injection, also known as a costovertebral block, is performed to alleviate upper back pain caused by damage or injury to the costovertebral joint. The costovertebral joint is located on either side of the vertebrae and connects the heads of the ribs with the vertebral bodies.
Cervical Arthroplasty

Arthroplasty is a surgical procedure to restore joint function by replacing a damaged joint with an artificial joint called a prosthesis.
Cervical arthroplasty is performed to replace the joints in the neck region of the spine. The vertebral bones of the spine are separated by soft discs which can undergo injury or degeneration. Cervical arthroplasty involves replacing these discs with artificial prostheses and is also called cervical disc replacement surgery.
Cervical Facet Blocks

A facet block is a procedure in which a combination of a local anesthetic and a corticosteroid is injected into a facet joint. A cervical facet block prevents the transmission of pain signals from the neck.
The facet joints are paired joints located at the back of the spine, which connect the adjacent vertebrae together and provide stability to the spine. The facet joints in the neck are referred to as cervical facet joints.
Cervical/Lumbar Traction

Excessive pressure on the spine from injury or stress may cause discs present between the vertebrae to herniate. Nerves exiting and entering the spine may become compressed by these herniated discs.
Traction or spinal decompression therapy separates the vertebrae and reduces the pressure on the nerves.
Cervical Spine Fusion

Your spine consists of a spinal cord supported by a series of interlocking bones called vertebrae. The cervical spine is the upper part of the spine situated in the neck region. It has seven vertebrae, separated and cushioned by spongy intervertebral discs. The vertebrae and discs may get damaged by injury, disease or wear-and-tear, compromising the cervical spine.
Cervical Laminoplasty

Degeneration of the facet joints and intervertebral discs that connect vertebrae to one another results in narrowing of the spinal canal, known as spinal stenosis. In addition, the arthritic facet joints become bulkier and consume the space existing for the nerve roots. Besides, thickened ligaments and bony outgrowths are also known as bone osteophytes or bone spurs can also narrow the spinal canal.
Cervical Medial Branch Block

A medial branch block is a procedure in which a mixture of a local anesthetic with or without a corticosteroid is injected near the medial branch nerves supplying a facet joint. A cervical medial branch block prevents the transmission of pain signals from the neck.
Cervical Laminectomy

Degeneration of the facet joints and intervertebral discs results in narrowing of the spinal canal known as spinal stenosis. In addition, the arthritic facet joints become bulkier and consume the space available for the nerve roots. Besides, bony outgrowths also known as bone spurs or bone osteophytes can also narrow the spinal canal.
Cervical Bracing

Cervical braces are external devices used to provide support and restrict movement of the cervical spine in a variety of cervical conditions ranging from muscle spasm to severe spine instability or post-surgery. Braces are also called orthotics and are made from different materials such as nylon, rubber, moulded plastic and elastic cotton.
Cervical Disc Replacement

One of the more common ailments facing the general population is neck pain. While there are many reasons for neck pain, typical causes include traumatic incidents, disc herniation(s) and also "wear and tear" conditions resulting in degenerative features such as arthritis that may crowd the spinal cord or nerve roots within the neck.
Cervical Foraminotomy

Cervical foraminotomy is a surgical procedure performed to relieve the symptoms of a pinched or compressed spinal nerve by enlarging the neural foramen, an opening for the nerve roots to exit the spine and travel through the body. The neural foramen forms a protective passageway for nerves that transmit signals among the spinal cord and the rest of the body parts.
Cervical Epidurals

A cervical epidural is an injection of medication into the epidural space in the lower section of the cervical region to provide relief from pain or inflammation affecting the neck and upper back. The epidural space is the space between the outermost covering of the spinal cord (dura mater) and the wall of the spinal canal and runs along the length of your spinal cord.
Cervical Laminectomy and Fusion

Cervical laminectomy is a surgical procedure in which the spinal canal is made larger by removing the spinous process and the lamina in the cervical region of the spine. This reduces neck pain and relieves the pressure on the spinal cord caused by the degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs in the cervical region.
Minimally Invasive Cervical Discectomy

The vertebrae of the backbone are cushioned by intervertebral discs that act as shock absorbers and allow frictionless movement of your back. It is made up of a soft gel-like center called the nucleus pulposus that is surrounded by a tough outer ring of annulus fibrosus. A herniated disc is a condition in which the nucleus pulposus bulges out through the damaged or broken annulus fibrosus.
Posterior Cervical Microforaminotomy/Discectomy

Posterior cervical microforaminotomy/discectomy is an operative procedure that relieves pressure or compression on the nerve roots at the cervical spine.
The cervical region (neck area) forms the upper portion of the spine. A series of cervical vertebrae, C1-C7 connects the cervical spine to the skull.
Posterior Cervical Foraminotomy

Posterior cervical foraminotomy is a surgical procedure performed through the back of the neck to relieve symptoms of a pinched or compressed spinal nerve by enlarging the neural foramen, an opening for the nerve roots to exit the spine and travel through the body, and creating more space for the spinal nerve to pass through. The neural foramen forms a protective passageway for nerves to transmit signals from the spinal cord to the rest of the body.
Posterior Cervical Decompression

Posterior cervical decompression is a surgical procedure performed through the back of the neck to relieve pressure over compressed nerves in the cervical spine region caused by inflamed spinal tissue or nerves, by removing portions of the cervical vertebrae. Injury or wear-and-tear can cause parts of the cervical vertebrae to compress the nerves of the spinal cord, leading to pain, numbness, or tingling in the part of the body that the nerve supplies.
Posterior Cervical Fusion

Posterior cervical fusion (PCF), a surgical procedure performed through the back of the neck, involves joining or fusing two or more damaged cervical vertebrae. The fusion of vertebrae is also known as arthrodesis. Sometimes, metallic plates may be used for fixing the vertebrae, this is also known as instrumentation.
PCF may be employed for the management of cervical fractures, bone dislocations and deformities due to an abnormal curvature of the cervical vertebrae.
Posterior Cervical Laminectomy and Fusion

Injury or wear-and-tear can cause parts of the cervical vertebrae in the neck region to compress the nerves of the spinal cord, leading to pain, numbness, or tingling in the part of the body that the nerve supplies.
Posterior cervical laminectomy and fusion is a surgical procedure performed through the back of the neck to relieve pressure over compressed nerves in the cervical spine region caused by inflamed spinal tissue or nerves.
Anterior Cervical Corpectomy and Fusion

An anterior cervical corpectomy and fusion is an operative procedure to relieve pressure on the spinal cord and spinal nerves by removing the vertebral bone and intervertebral disc material (decompression) in the cervical spine or neck.
Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement

Disc degeneration reduces the height of the disc and may cause a Herniated disc. The vertebrae of the backbone are cushioned by intervertebral discs that act as shock-absorbers and allow frictionless movement of your back. It is made up of a soft gel-like center called the nucleus pulposus that is surrounded by a tough outer ring of annulus fibrosus. A herniated disc is a condition in which the nucleus pulposus bulges out through the damaged or broken annulus fibrosus.
Cervical Corpectomy and Strut Graft

The cervical spine comprises of the first 7 vertebrae of the spinal column. The vertebrae are separated from one another by shock-absorbing pads called intervertebral discs. Over time, the discs can become worn out and can result in neck pain.
Cervical Microdiscectomy

Your spine consists of 24 bones called vertebrae that are arranged one above the other and separated by intervertebral discs which act as shock absorbers during activity. Your neck or cervical area is made up of seven of these vertebrae.
Multilevel Posterior Cervical Laminectomy and Fusion

Posterior cervical laminectomy and fusion is an operative procedure to relieve pressure or compression on the nerve structures due to herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or spondylosis. It is often performed for multilevel spinal cord compression from cervical spinal stenosis to decompress the spinal cord and nerve roots in the cervical region (neck region) of the spine.
Lumbar Fusion

Spinal fusion, also called arthrodesis, is a surgical technique used to join two or more vertebrae (bones) within the spine. Lumbar fusion is the procedure of fusing the vertebrae in the lumbar portion of the spine (lower back). A piece of bone, taken from other parts of the body or donated from a bone bank is transplanted between the adjacent vertebrae. Screws, plates, or cages may be used with the bone graft to help hold the spine.
Lumbar Laminectomy

Lumbar laminectomy is a spinal surgery to relieve excess pressure on the spinal cord or nerves within the spinal canal in the lumbar or lower back region. The pressure may be caused by bony overgrowths, herniated discs, injury, tumors, or narrowing of the spinal canal resulting in painful symptoms affecting a person’s ability to perform normal day to day activities.
Lumbar Foraminotomy

Conditions such as a herniated intervertebral disc or bony overgrowth may cause compression of the spinal nerves as they pass through the neural foramen. In the lower back or lumbar region, this can result in lower back pain as well as pain, weakness, and numbness in the legs.
Lumbar Artificial Disc Replacement

Lumbar artificial disc replacement is a surgical procedure employed to remove and replace a damaged or worn out disc in the lumbar or lower part of your spine that has become painful and debilitating with an artificial or synthetic disc. An artificial disc is made of metal or plastic or a combination of both and is designed to support the vertebrae while still allowing forward and backward bending, side-to-side bending, and turning. The main objective of the procedure is to relieve back pain and maintain normal motion of the lumbar spine.
Lumbar Decompression

The spinal cord is protected by a bony column of vertebral bones, arranged one above the other. Injury or wear-and-tear can cause parts of the vertebrae to compress the nerves of the spinal cord, leading to pain, numbness or tingling in the part of the body that the nerve supplies.
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Discectomy

Lumbar discectomy is a spinal surgery that involves the removal of the damaged intervertebral disc(s) to relieve pressure on the spinal nerves (decompression) in the lumbar (lower back) region, which forms the lower portion of the spine and comprises of five vertebrae (L1-L5). A minimally invasive technique is implemented to perform the surgery.
Lumbar Sympathetic Block

Sympathetic nerves located in the lower spine control basic functions such as regulating blood flow. They also carry pain signals from tissues to the spinal cord.
A lumbar sympathetic block is an injection of a local anesthetic and steroid that is injected into or around the sympathetic nerves to block the transmission of pain impulses from the legs or lower back, thereby relieving pain.
Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF)

Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) is a type of spinal fusion procedure in which bone graft is placed between the affected vertebrae in the lower back (lumbar) region through an incision on the patient’s back.
Posterior Lumbar Fusion

Spinal fusion, also called arthrodesis, is a surgical technique used to join two or more vertebrae (bones) within the spine. Lumbar fusion is the fusion the vertebrae in the lumbar portion of the spine (lower back).
Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion

The back is made up of a number of small bones called vertebrae. Cushioning discs present between the vertebrae act as shock absorbers. The vertebral column allows the cylindrical bundle of nerve fibers called the spinal cord to pass through the entire column length and branch out to the various parts of the body.
Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion

Spinal fusion is a surgical technique that joins two or more vertebrae in the spine to minimize the pain caused by the movement of these vertebrae. The fusion of vertebrae in the lumbar portion of the spine is called lumbar fusion. This surgery can be performed as an open or minimally invasive procedure.
Posterolateral Lumbar Fusion

Posterolateral lumbar fusion is a surgical technique that involves correcting spinal problems from the back of the spine by placing bone graft between segments in the back and leaving the disc space intact.
Minimally invasive surgical techniques may be used to perform the procedure.
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Surgery

Spinal surgery can be performed by two different approaches; one is the conventional open surgical approach and the other is the advanced minimally invasive approach. Each approach has its own advantages and preferences. However, the minimally invasive technique is a more advanced approach with a higher success rate and a minimal level of patient discomfort.
Lumbar Corpectomy and Fusion

Lumbar corpectomy and fusion is a surgical technique performed to remove the vertebral bone or disc material between the vertebrae to alleviate pressure on the spinal cord and spinal nerves (decompression) in the lumbar (lower back) region.
Lumbar Facetectomy and Foraminotomy

The vertebrae (spinal bones) have openings known as neuroforamen on either side for the passage of spinal nerves. The neuroforamen are surrounded by tiny joints known as facet joints, present in pairs at the back of each vertebra, which connect and stabilize them together. Bone spurs herniated intervertebral disc material, and thickened ligaments can obstruct the neuroforamen, causing compression of the nerves, and pain in your arms and legs.
Lumbar Facet Block

A facet block is a procedure in which a combination of a local anesthetic and a corticosteroid is injected into a facet joint. A lumbar facet block prevents the transmission of pain signals from the lower back.
Lumbar Interbody Fusion

Lumbar interbody fusion (LIF) surgery is a surgical technique that involves the removal of a damaged intervertebral disc and the insertion of a bone graft into the disc space created between the two adjoining vertebrae. Bone grafts promote healing and facilitate fusion. Screws and rods are used to stabilize the spine during the healing process.
Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion

Anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) is a surgery performed to correct spinal problems in the lower back. The surgery can be implemented either as an open surgery or minimally invasive technique.
Lower Back (Lumbar) Surgery

Lower back pain is one of the most common health problems experienced by most individuals, at different phases of their lives.
Lumbar Microdiscectomy

Microdiscectomy is a surgical procedure employed to relieve the pressure over the spinal cord and/or nerve roots, caused by a ruptured (herniated) intervertebral disc. A herniated disc, common in the lower back (lumbar spine) occurs when the inner gelatinous substance of the disc escapes through a tear in the outer, fibrous ring (annulus fibrosis). This may compress the spinal cord or the surrounding nerves, resulting in pain, sensory changes, or weakness in the lower extremities.
Minimally Invasive TLIF

The spine is made up of small bony segments called vertebrae. These vertebrae are categorized into cervical or neck vertebrae, thoracic (upper back) and lumbar (lower back). Cushioning discs present between each vertebra act as shock absorbers. A cylindrical bundle of nerve fibers called the spinal cord passes through the entire vertebral column and branches out to the various parts of our body.
Lumbar Spinal Bracing

Lumbar braces are external devices used to restrict the movement of the lumbar spine and provide support and stability to the lower back region, to relieve back pain and promote healing after surgery or injury.
Lumbar Spinal Fusion

The surgical technique of combining two or more vertebrae is known as spinal fusion. Back pain due to abnormal motion of the vertebrae is treated by this procedure. Fusion of the vertebrae involves the insertion of secondary bone tissue obtained either through autograft (tissues from the same patient) or allograft (tissues from another person) to enhance the natural osteoblastic process of the body.
Lumbar Discectomy

The lower back or lumbar region is often the site of pain due to its high mobility and weight-bearing. Spongy discs present between the vertebral bones of the spine help cushion the spine during stress and movement. These intervertebral discs in the lumbar region may undergo damage due to stress, causing them to herniate or rupture, and compress adjacent spinal nerves. This can lead to lower back pain, as well as pain, weakness, and numbness in the lower legs.
Lumbar Epidurals

Lumbar epidurals are injections to treat and relieve low back pain. A lumbar epidural involves injecting a local anesthetic and an anti-inflammatory steroid into the epidural space of the lower spine (lower back) to reduce inflammation causing the pain.
Lumbar Medial Branch Block

A medial branch block is a procedure in which a mixture of a local anesthetic with or without a corticosteroid is injected near the medial branch nerves supplying a facet joint. A lumbar medial branch block prevents the transmission of pain signals from the lower back.
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Decompression

Minimally invasive lumbar decompression or mild® is a procedure developed by Vertos Medical to treat lumbar spinal stenosis by relieving pressure on the spinal nerves.
Lumbar spinal stenosis is a degenerative disease that usually occurs after the age of 50. It causes narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal and compression of the spinal nerves.
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion

Spinal fusion is a surgical technique used to join together two or more vertebrae in the spine and to minimize the pain caused by the movement of these vertebrae. The fusion of vertebrae in the lumbar portion of the spine is called lumbar fusion and the surgery can be done as an open or minimally invasive procedure.
Anterior Lumbar Corpectomy and Fusion

Anterior Lumbar Corpectomy and Fusion is a surgical technique performed to remove the vertebral bone or disc material between the vertebrae to alleviate pressure on the spinal cord and spinal nerves (decompression) in the lumbar (lower back) region.
Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion (OLIF)

The lumbar spine is made up of 5 bones, arranged one above the other and separated by spongy intervertebral discs that cushion the spine during movement.
As vertebral bones age, the discs go through wear and tear, leading to damage and degeneration of the discs. This further causes the bones to rub painfully against each other.
Radiofrequency Ablation for Lumbar Spondylosis

Radiofrequency ablation for lumbar spondylosis is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed to treat lower back pain secondary to lumbar spondylosis. The procedure employs radiofrequency waves to produce heat which damages the nerves transmitting pain signals to the brain in the lumbar spine.
In-Office Lumbar Injections

In-office lumbar injections are steroid shots administered to you in your physician’s clinical or office setting to relieve low back pain. These shots involve injecting a local anesthetic and an anti-inflammatory steroid into the lumbar (lower back) area of your spine. Your doctor decides on the appropriate injection depending on the source of the pain in your lumbar area.
Thoracic Discectomy

The human spine provides support to the body allowing you to stand upright, bend, and twist. The spine can be broadly divided into the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine. The thoracic spine lies in the mid-back region between the neck and lower back and is protected by the rib cage.
Thoracic Facetectomy

The spinal cord passes through the vertebral column, which forms a bony protective cover. At the thoracic region (upper back), the spinal canal is especially narrow when compared to the neck and lower back regions, making it more susceptible to compression.
Thoracic Laminectomy

The vertebral column supports the back and protects the spinal cord that runs through it. The nerves that branch out from the spinal cord are also protected and pass through special passages created by each vertebral bone. However, degeneration or herniation (bulging out) of the intervertebral disc that cushions each vertebral bone, injury, bony outgrowths due to arthritis or tumors can compress the spinal cord and nerves, causing debilitating back pain and disability.
Thoracic Spine Decompression

Coming soon
Thoracic Spine Fracture Repair Surgery

Spinal fractures occur most commonly in the thoracic (upper back) and lumbar (lower back) regions, and at the thoracolumbar junction. Fractures in these regions can occur due to injury from falls, motor vehicle accidents, violent acts and sports accidents, and also from the degeneration of bones due to old age and disease (osteoporosis and tumors). Thoracic spine fracture repair surgery is a treatment option to repair spinal fractures.
Thoracic Spine Revision Surgery

Revision spine surgery is performed to correct the problems of earlier spine surgery. It is considered when you do not obtain relief from pain following the initial surgery. O
Thoracic Spine Trauma Surgery

Coming soon
Thoracic Tumor Surgery (Intradural and Extradural)

Trauma to the spine can injure the vertebral bones as well as the spinal cord and spinal nerves. Spine trauma is a common injury and may be caused by falls, sports, the low impact falls in the elderly due to osteoporosis, assault, and motor vehicle accidents. Trauma can lead to fractures and dislocations of bones, rupture of ligaments, damage to intervertebral discs, vascular injury, compression of spinal nerves, or bruising or tearing of the spinal cord.
Thoracic Vertebroplasty

The spinal cord passes through the vertebral column, which forms a bony protective cover. However, a spinal tumor can compress the spinal cord or spinal nerves, leading to pain, loss of sensation, and/or motor function in the part of the body supplied by the compressed nerve. Thoracic vertebrectomy is the surgical removal of the vertebrae to decompress the nerve and restore function.
Thoracic Vertebrectomy

The spinal cord passes through the vertebral column, which forms a bony protective cover. However, a spinal tumor can compress the spinal cord or spinal nerves, leading to pain, loss of sensation, and/or motor function in the part of the body supplied by the compressed nerve. Thoracic vertebrectomy is the surgical removal of the vertebrae to decompress the nerve and restore function.
Posterior Thoracic Fusion

Posterior thoracic fusion is a spinal fusion procedure performed through an incision on the back (posterior) of the patient in which two or more vertebrae of the thoracic spine (mid back) are joined together, eliminating any movement between them. This procedure is performed by placing bone grafts or bone graft substitutes in between the affected vertebrae to promote bone growth and eventually fuse the vertebrae into a single, solid bone.
Thoracic Corpectomy

Thoracic corpectomy is a surgical procedure performed to relieve pressure on a nerve at the thoracic region (upper and middle back) by removing the source of the compression.
The thoracic spine is the central part of the spine. The spine consists of 33 vertebral bones stacked one on top of the other with cushioning discs lying between each vertebrae.
Computer Navigated Thoracic Spine Surgery

The spine is a complex 3- dimensional structure that is interspersed with a complex lattice of delicate blood vessels and nerves. Trauma to these structures during surgery is a big concern in spinal surgery. The complexity and increased need for precision in thoracic spine surgeries have led to the introduction of computers to assist in many spinal procedures.
Preventing Back Pain at Home and Work

The back is subject to wear and tear from daily activities and stresses. Pain may vary in severity and duration. Although the natural degenerative processes that take place with aging cannot be avoided, precautions can be taken at home and your workplace to minimize its impact. A healthy lifestyle with good habits such as regular exercise, adequate sleep, good posture, a diet adequately supplemented with calcium and vitamin D, and avoiding weight gain, smoking, and stress can go a long way in keeping the back healthy.
Am I a Candidate for Spine Surgery?

Spinal issues manifest in a large number of people at all phases of life. Back pain is one of the most common complaints that individuals visit a doctor for. Many orthopedic issues such as arthritis and other joint problems are manifested in the spine. Improper body mechanics, aging, trauma, and structural abnormalities can harm your spine, leading to back pain and other symptoms.
Back and Neck Braces

The spine is composed of spinal bones called vertebrae, intervertebral discs, connective tissue, and muscles. All of these structures provide support, stability, and mobility to the upper body. The spine also protects the delicate spinal cord. Injury or disease to any of these structures can cause pain.
Medications

Medications play an effective role in the treatment of back or neck pain. Your doctor may prescribe several medications to help reduce pain and associated symptoms that are caused by unhealthy spinal conditions or deformities.
Back Pain Exercises

Strenuous activities of daily living can stress the back resulting in pain. It is natural at this time to withdraw from activity and rest, but is not helpful in the long run and may actually slow down the healing process.
Nutrition and Your Spine

Nutrients are the chemical components present in food, which provide energy for carrying out normal physiological functions and aid in various metabolic processes of the body.
Nutrition refers to the entire cycle of chemical changes occurring within the body based on what we eat or don’t eat. It determines the strength of the teeth, bones and the connective tissues.
Spine Medications

Medications play an effective role in the treatment of back or neck pain. Your doctor may prescribe several medications to help reduce pain and associated symptoms that are caused by unhealthy spinal conditions or deformities.
Complications of Spinal Surgery

The most serious complication of a herniated disc that may occur before surgery is the development of the cauda equine syndrome. It occurs when a large particle of disc material ruptures in the spinal canal. It occurs in the area where the nerves that control the bowels and bladder travel before they leave the spine.
Recovery and Post-op Instructions after Spine Surgery

The duration of hospitalization depends on the treatment rendered. The period of your rest or inactivity depends on a few factors such as the type of surgical procedure and the approach used to access your hip, the size of the incision and presence of any complications. Return to work or normal activity depends on the type of work or activity you plan to perform.
Spine Comprehensive Medicine

Spine comprehensive medicine involves comprehensive care of acute or chronic neck or back injuries or conditions. It aims at minimizing your pain, making you as functional as possible and preventing future injury.
Spine Rehabilitation

Dysfunction of the spine can be severely debilitating to one’s ability to perform activities at both home and work. Pain in the lumbar spine (lower back) is the number one reason for missed days of work, followed by the pain of the cervical spine (neck).
Healthy Back Tips

Back and neck pain is the most common health problems experienced by most people, at some point in their lives. People with back pain or neck pain may have trouble performing daily routine activities.
There are several things that you can do to relieve stress and lessen your back and neck pain.
Proper Lifting

Lifting heavy weights and improper lifting of weights is one of the foremost causes of neck pain or lower back pain. Practicing proper lifting techniques is essential to avoid strain on your neck and back.
Prior to lifting weights, stretch slowly and stop lifting weights if you experience any sharp pain.
Possible Complications of Spinal Surgeries

The most serious complication of a herniated disc that may occur before surgery is the development of the cauda equine syndrome. It occurs when a large particle of disc material is ruptured into the spinal canal. It occurs in the area where the nerves that control the bowels and bladder travel before they leave the spine. This causes pressure on these nerves resulting in permanent damage. Bowel and bladder controlling ability are lost. If this problem occurs, surgery could be recommended immediately to try to remove the pressure on the nerves.















